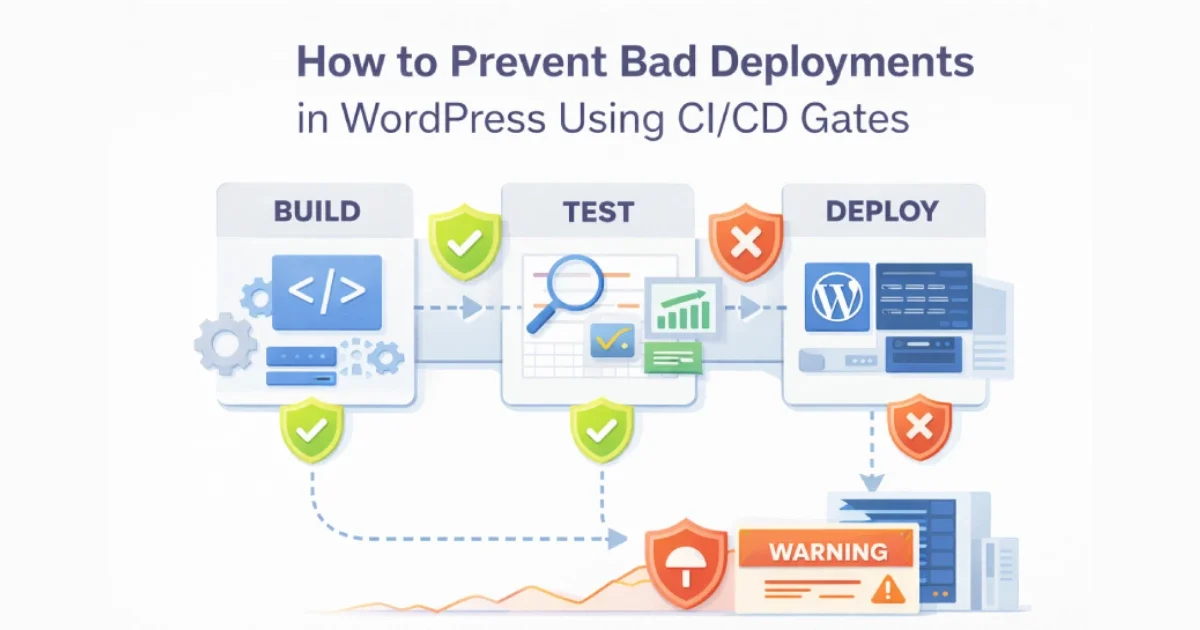
Bad deployments are one of the most common causes of WordPress outages, regressions, and security incidents. A broken plugin update, a missing environment variable, or an untested configuration change can take a site down in seconds. The problem is rarely WordPress itself — it’s uncontrolled releases.
CI/CD gates exist to stop bad changes before they reach production.
At Wisegigs.eu, every production WordPress deployment passes through multiple automated gates designed to catch failures early, cheaply, and safely. This guide explains how to design CI/CD gates that prevent bad deployments while keeping release velocity high.
1. What CI/CD Gates Actually Are
A CI/CD gate is a hard stop in your deployment pipeline.
If a condition fails, the pipeline stops — no deploy, no partial release, no “we’ll fix it later.”
Gates typically validate:
Code quality
Security posture
Configuration correctness
Runtime compatibility
Deployment safety
Gates turn deployments from a manual risk into a controlled system.
GitLab defines gates as a core mechanism for enforcing quality and security in modern pipelines:
https://about.gitlab.com/topics/ci-cd/
2. Why WordPress Deployments Fail in the First Place
Most WordPress deployment failures follow predictable patterns.
Common causes:
Plugin or theme updates pushed directly to production
Environment variables missing or misconfigured
PHP version incompatibilities
Database migrations not considered
Caching layers not cleared or invalidated correctly
Dependency conflicts
No rollback strategy
Without gates, these problems slip through silently.
At Wisegigs.eu, any change that bypasses CI/CD is considered a production risk.
3. Gate #1: Version Control Enforcement
The first gate is not technical — it’s procedural.
Required rules:
No direct production edits
All changes must go through Git
Protected main/production branches
Mandatory pull/merge requests
Required peer review
This gate alone prevents:
Accidental changes
Untracked fixes
Emergency edits that cause long-term instability
GitHub’s branch protection rules are designed specifically to prevent unsafe releases:
https://docs.github.com/en/repositories/configuring-branches-and-merges-in-your-repository
4. Gate #2: Environment Parity Checks
Many deployments fail because local ≠ staging ≠ production.
Gate should verify:
PHP version compatibility
Required PHP extensions
Environment variables present
File system permissions
Correct wp-config behavior per environment
Smashing Magazine emphasizes that environment parity eliminates “works on my machine” failures:
https://www.smashingmagazine.com/
A deployment should never discover environment problems after going live.
5. Gate #3: Dependency & Update Validation
WordPress sites are dependency-heavy systems.
Gate validations:
Plugin compatibility with current WP version
Theme compatibility
Deprecated function usage
Abandoned plugin detection
Known vulnerability checks
WP Tavern frequently reports incidents caused by outdated or abandoned plugins:
https://wptavern.com/
This gate blocks risky updates before users feel the impact.
6. Gate #4: Security Scanning
Security issues introduced during deployment are often invisible at first.
Security gates should check:
Known vulnerable dependencies
Accidental secret exposure
File permission regressions
Unauthorized file changes
OWASP highlights that CI/CD pipelines are a primary defense against supply-chain attacks:
https://owasp.org/www-project-top-ten/
At Wisegigs.eu, security scanning is mandatory — not optional — for every release.
7. Gate #5: Performance Regression Protection
Not all bad deployments cause downtime — many cause slowdowns.
Performance-related gates:
PHP execution time thresholds
Cache hit ratio checks
Asset size regression detection
Build size changes
Page generation timing
Cloudflare explains that small latency increases often precede major performance incidents:
https://www.cloudflare.com/learning/performance/
A deployment that slows the site is still a failed deployment.
8. Gate #6: Staging Verification (Pre-Production)
Staging is not a checkbox — it’s a validation layer.
Staging gate requirements:
Same infrastructure as production
Same caching layers
Same CDN rules
Same environment variables
Same plugin set
Only after staging validation should production deployment be allowed.
At Wisegigs.eu, production deploys are impossible unless staging passes all gates.
9. Gate #7: Deployment Safety & Rollback Readiness
A deployment is not safe unless it can be undone.
Final gate checklist:
Atomic deployment strategy
Previous release still available
Rollback tested regularly
Database changes reversible or backward-compatible
Deployment logs enabled
Google’s SRE book stresses that fast rollback is more important than fast deploys:
https://sre.google/sre-book/
If rollback isn’t ready, deployment should not proceed.
10. CI/CD Gates Improve Speed, Not Just Safety
Many teams fear gates will slow them down. In practice, the opposite happens.
Benefits:
Fewer emergency fixes
Less downtime
Faster recovery
More confident releases
Predictable deployment windows
Gates replace anxiety with certainty.
Conclusion
Bad deployments are not random events — they are the result of missing controls. CI/CD gates turn WordPress deployments into a disciplined, repeatable system where risky changes are stopped early and safely.
To recap:
Enforce Git-based workflows
Validate environment parity
Block risky dependencies
Scan for security issues
Detect performance regressions
Require staging validation
Ensure rollback readiness
Want to eliminate risky WordPress deployments and build a safer CI/CD pipeline? Contact Wisegigs.eu.